Methods of flue gas waste heat recovery
DOWNLOAD
Methods of flue gas waste heat recovery
Two methods are usually adopted for flue gas waste heat recovery: one is to preheat the workpiece; The other is to preheat air for combustion. The flue gas preheating of workpieces needs to occupy a large volume for heat exchange, which is often limited by the operation site (this method cannot be used for intermittent furnaces). Preheating air for combustion support is a good method. It is generally configured on the heating furnace, which can also strengthen combustion, speed up the temperature rise of the furnace and improve the thermal performance of the furnace. This can not only meet the requirements of the process, but also achieve significant comprehensive energy-saving effect.
In addition, preheaters of preheated air have been used in industrial furnaces and kilns in China since the 1950s, mainly in the form of tubular, cylindrical radiant and cast iron block heat exchangers, but the exchange efficiency is low. In the 1980s, domestic heat exchangers such as jet type, jet radiation type and double table type were developed successively to mainly solve the waste heat recovery of medium and low temperature. Remarkable results have been achieved in the waste heat recovery of flue gas below 100 ℃, and the heat exchange efficiency has been improved. However, at high temperature, the material of heat exchanger is still limited, the service life is low, the maintenance workload is large or the solid cost is expensive, which affects the promotion and use.
At the beginning of the 21st century, a ceramic heat exchanger was developed in China. Its production process is basically the same as that of kiln furniture. Thermal conductivity and oxidation resistance are the main application properties of materials. Its principle is to place the ceramic heat exchanger near the flue outlet where the temperature is relatively high, without mixing cold air and high temperature protection. When the furnace temperature is 1250-1450 ℃, the temperature of the flue outlet should be 1000-1300 ℃. The ceramic heat exchanger can recover waste heat up to 450-750 ℃. The returned hot air is sent to the furnace to form mixed gas with gas for combustion, which can save energy by 35% - 55%, thus directly reducing production costs, Increase economic benefits.
Ceramic heat exchanger has been well developed under the use limitation of metal heat exchanger, because it has better solved the problems of corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance, and has become the best heat exchanger for recovering high temperature waste heat. After many years of production practice, it shows that the ceramic heat exchanger has a good effect. Its main advantages are: good thermal conductivity, high temperature strength, good oxidation resistance and thermal shock resistance. Long service life, small maintenance, reliable and stable performance, simple operation. It is the best device for recovering waste heat of high-temperature flue gas at present. At present, ceramic heat exchangers can be used in major thermal kilns in metallurgy, non-ferrous, refractory, chemical, building materials and other industries.
Other methods of flue gas waste heat recovery:
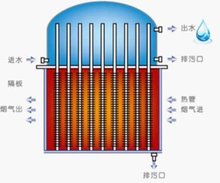
1. Waste heat recovery device (gas water)
The heat pipe waste heat recovery device is a special equipment for coal fired, oil fired and gas fired boilers. It is installed at the boiler flue to recover waste heat from flue gas to heat domestic water or boiler make-up water. Its structure is as shown in the figure: the lower part is a flue, the upper part is a water tank, and there is a partition in the middle. The top is equipped with safety valve, pressure gauge and thermometer interface, and the water tank is equipped with water inlet and outlet and drain outlet. During operation, the flue gas flows through the flue of the heat pipe waste heat recovery device to wash the lower end of the heat pipe. After the heat pipe absorbs heat, it conducts the heat to the upper end, and the upper end of the heat pipe releases heat to heat the water. In order to prevent ash blockage and corrosion, the flue gas temperature at the outlet of the waste heat recovery device is generally controlled above the dew point, that is, the flue gas temperature of fuel oil and coal-fired boilers is not less than 130 ℃, and the flue gas temperature of gas boilers is not less than 100 ℃, saving 4-18% of fuel.
2. Waste heat recovery device (gas gas)
The heat pipe waste heat recovery device is a special equipment for oil fired, coal fired and gas fired boilers. It is installed in the boiler flue or flue to heat the air after recovering the waste heat of flue gas. The hot air can be used as combustion supporting and drying materials for the boiler. Its structure is as shown in the figure: the channels on both sides are separated by the surrounding pipe box and the middle partition plate. The heat pipe is a full finned pipe, and a single heat pipe can be replaced. During operation, high-temperature flue gas flows upward from the left channel to wash the heat pipe. At this time, the heat pipe absorbs heat and the flue gas heat release temperature drops. The heat absorbed by the heat pipe will lead to the right end, and the cold air will wash the heat pipe backward from the right channel. At this time, the heat pipe will release heat, and the air heat absorption temperature will rise. The flue gas temperature at the outlet of the waste heat recovery device shall not be lower than the dew point.

3. Waste heat ammonia absorption refrigeration
The absorption refrigeration unit that uses ammonia as the refrigerant and water as the absorbent to realize solution circulation is the ammonia water absorption refrigeration unit. Because ammonia is used as the refrigerant, the refrigeration temperature range is from - 30 to 5 degrees centigrade, and the application range is very wide. Waste heat recovery refrigeration can be used as air conditioner or industrial cold source. After nearly 10 years of research, Taishan Group has made some achievements in this regard.

